Contents
Advertisement
Advertisement
Introduction
Definition
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) accounts for 90% to 95% of malignant neoplasms arising from the kidney. Recent advances in surgical and systemic therapies have significantly changed the management of RCC. Targeted therapies against the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) pathway have extended the lives of the patients with advanced disease significantly, with median overall survival currently exceeding 2 years.1
Epidemiology
RCC accounts for 2% to 3% of all malignant diseases in adults. It is the seventh most common cancer in men and the ninth most common in women. In the United States, there are approximately 65,000 new cases each year and about 13,500 deaths from RCC annually.2 The incidence of RCC in the US has increased over time.3-5 Between 1992 and 2005, the incidence rose by 1.8% and 2.1% among white men and white women, respectively, and by 2.1% and 1.7% among black men and black women, respectively. In an analysis of more than 29,000 cases from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) database, this increased incidence has been associated with a steady decrease in the average size of tumors at presentation (6.7 cm vs 5.9 cm in 1988 and 2002, respectively).3 Despite the earlier detection of smaller kidney tumors, the rate of RCC-related mortality has increased,6,7 suggesting that recurrence and advanced disease are responsible for mortality.
Within the US, Asian Americans and Pacific Islanders have the lowest incidence of renal cancers compared with American Indians/Alaskan natives, Hispanics, Caucasians, and African Americans.2 Globally, the incidence of RCC varies widely from region to region, with the highest rates observed in the Czech Republic and in North America.8
RCC is approximately 50% more common in men than in women.9 It usually occurs between the sixth and eighth decades of life, with a median age of 65.
Table 1: Renal Cell Carcinoma Risk Factors |
| Tobacco smoking |
| Obesity |
| Hypertension |
| Occupational exposures |
| Polycystic kidney disease |
| Chronic Hepatitis C infection |
| Genetic |
Risk Factors
Inhaled tobacco smoke is clearly implicated in the etiology of RCC, with a strong dose-dependent increase in risk associated with numbers of cigarettes smoked per day and a substantial reduction in risk for long-term former smokers.10 Higher body mass index (BMI) and elevated blood pressure independently increase the long-term risk of renal cell cancer in men. A reduction in blood pressure has been associated with a reduced risk of RCC.11 These 3 risk factors together are associated with 49% of cases.12
Other modifiable risk factors, although not convincingly associated, include exposure to asbestos, trichloroethylene, or thiazide, and use of acetaminophen or other analgesic drugs. Renal cell carcinoma also seems to be more common in patients with chronic hepatitis C infection,13 end-stage renal failure, acquired renal cystic disease,14 and tuberous sclerosis15 than in the general population (Table 1).
Detection & Diagnosis
Genetics
Individuals with a family history of RCC have a 2.8-fold greater chance for developing renal cancer during their lifetimes16 and account for about 4% of all RCC cases. Studies of families with inherited RCC have enabled the identification of 6 hereditary RCC syndromes: von Hippel-Lindau (VHL), hereditary papillary renal carcinoma (HPRC), Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome (BHD), hereditary leiomyomatosis RCC (HLRCC), succinate dehydrogenase (SDH)-associated familial cancer, and tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC) (Table 2). The predisposing genes associated with these syndromes are VHL, MET, FLCN, FH, SDH, TSC1 and TSC2, respectively.17
Table 2: Hereditary Renal Cell Carcinoma Syndromes
| Syndrome | Gene (Chromosome) | Histology | Major clinical manifestations |
|---|---|---|---|
| von Hippel-Lindau | VHL tumor suppressor gene (3p25-26) | Clear cell | Autosomal dominant, retinal angioma, CNS hemangioblastomas, pheochromocytomas, pancreatic islet cell tumors, paragangliomas, cystadenoma of broad ligament or epididymis. |
| Hereditary papillary renal carcinoma | MET proto-oncogene (7q31) | Type 1 papillary | Autosomal-dominant, multifocal, bilateral renal cell tumors. |
| Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome | FLCN tumor suppressor gene (17p11.2) | Chromophobe, hybrid oncocytoma | Autosomal-dominant, cutaneous fibro-folliculoma, pulmonary cysts and spontaneous pneumothorax. |
| Hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell carcinoma | FH tumor suppressor gene (1q42-43) | Type 2 papillary | Autosomal-dominant, leiomyomas of skin and uterus, unilateral, solitary, and aggressive renal cell tumors. |
| Succinate dehydrogenase (SDH)-associated familial cancer40 | SDH-B subunit (1p35-36) SDH-D subunit (11q23) |
Clear cell, chromophobe, papillary type 2, renal oncocytoma | Head and neck para-ganglioma, and adrenal or extra-adrenal pheochromocytomas. |
| Tuberous sclerosis complex | TSC1 (9q34) TSC2 (16p13) |
Clear cell (common) | Autosomal-dominant, facial angiofibromas, multifocal renal angiolipomas, neurologic disorders or seizures, lymphangiomyomatosis of the lungs. |
| Adapted from The Lancet Vol. 373, Rini BI, Campbell SC, Escudier B, Renal Cell Carcinoma, pages 1119-1132, Copyright 2009, with permission from Elsevier. | |||
Pathophysiology
RCC consists of a heterogeneous group of tumors with distinct genetic and metabolic defects, as well as histopathologic and clinical features (Table 3).17 Medullary carcinomas are rare but aggressive, and are exclusively associated with sickle cell trait.
Table 3: Histologic Classification of Renal Cell Carcinoma
| Histology | Frequency | Cell of Origin | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clear cell | 60%-70% | Proximal tubule | Cells with clear cytoplasm with acinar or sarcomatoid growth pattern. |
| Papillary | 5%-15% | Proximal tubule | Type I: papillae lined with a layer of tumor cells with scant pale cytoplasm and low-grade nuclei. Type II: abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm and large pseudo stratified nuclei with prominent nucleoli; aggressive subtype. |
| Chromophobic | 5%-10% | Cortical collecting duct | Cells are large with finely reticulated eosinophilic cytoplasm, and atypical nuclei with perinuclear halo with solid, tubular or sarcomatoid growth pattern; indolent course. |
| Oncocytic | 5%-10% | Cortical collecting duct | Benign neoplasms. |
| Collecting duct | <1% | Medullary collecting duct | Papillary or sarcomatoid growth pattern. |
| Adapted from The Lancet Vol. 373, Rini BI, Campbell SC, Escudier B, Renal Cell Carcinoma, pages 1119-1132, Copyright 2009 with permission from Elsevier. | |||
Advertisement
Signs and Symptoms
Renal cancers have been called “the internist’s tumor” and are among the great mimics in medicine because they present with systemic symptoms unrelated to the kidney cancer, such as hypertension (renin), hypercalcemia (PTHrP), polycythemia (erythropoietin), eosinophilia, leukemoid reactions, Cushing’s syndrome (ACTH), fever or wasting syndromes, and Stauffer’s syndrome (reversible hepatic dysfunction after primary tumor removal). Most cases of RCC are diagnosed incidentally on radiographic investigation done for other reasons. The classic triad of hematuria, abdominal pain, and a palpable mass is present in ≤ 10% of cases.
Signs or symptoms resulting from metastatic disease include bone pain, adenopathy, pulmonary symptoms attributable to lung parenchyma or mediastinal metastases, upper GI bleed, and neurologic deficits.
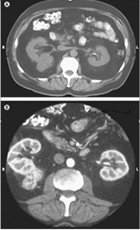
|
Figure 1. CT Scan of a Patient with Renal Cell Carcinoma Before (A) and After (B) Intravenous Contrast. Reprinted with permission from Saunders Elsevier (Campbell SC, Novick AC, Bukowski RM. Renal tumors. In: Kavoussi LR, Novick AC, Partin AW, et al, eds. Campbell-Walsh Urology. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders Elsevier; 2007:1571). Copyright © 2007 Elsevier. |
Diagnosis
The initial workup consists of taking a detailed medical history and performing a physical examination. Appropriate laboratory investigations include a complete blood cell count, a comprehensive metabolic panel (including evaluation of serum calcium level, liver function, and lactate dehydrogenase and serum creatinine levels), a coagulation profile, and urinalysis. Imaging studies should include computed tomography (CT) scans of the abdomen and pelvis (with and without contrast) (Figure 1) and chest imaging (either chest radiograph or CT scan).
Abdominal magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is used to evaluate tumor extension into the inferior vena cava. MRI can be used instead of CT when contrast media cannot be administered due to allergy or renal insufficiency.18,19 A bone scan or brain imaging is not routinely performed unless signs or symptoms suggest involvement of these areas. PET is not used to diagnose or follow up kidney cancer in any circumstance.20 Needle biopsy is not routinely used to establish diagnosis in patients with large renal masses and radiologic characteristics of malignancy. These patients often undergo immediate kidney removal, which is both diagnostic and therapeutic. However, needle biopsy may be valuable in patients with small (< 3 cm) renal masses not requiring nephrectomy.21
A differential diagnosis of urothelial carcinoma should be considered in a patient with a central renal mass and urine cytology. Alternatively, ureteroscopy should be pursued in addition to biopsy, as indicated.
The severity of disease is staged on the basis of imaging studies and the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) Cancer Staging Manual (Table 4). Approximately 50% of RCC patients present with localized disease, 25% with locally advanced disease, and 25% to 30% with metastatic disease.
Table 4: American Joint Committee on Cancer TNM Staging System for Kidney Cancer
| Primary Tumor (T) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tx | Primary tumor can not be assessed | |||
| T0 | No evidence of primary tumor | |||
| T1a | Tumor ≤ 4 cm, confined to the kidney | |||
| T1b | Tumor 4 cm to < 7 cm, confined to the kidney | |||
| T2a | Tumor ≥ 7 cm to < 10 cm, confined to the kidney | |||
| T2b | Tumor ≥ 10 cm, confined to the kidney | |||
| T3a | Tumor extends into the renal vein or its segmental branches or invades adrenal gland or perinephric fat but not beyond Gerota’s fascia | |||
| T3b | Tumor extends into the vena cava below diaphragm | |||
| T3c | Tumor extends into the vena cava above the diaphragm or invades the wall of vena cava | |||
| T4 | Tumor invades beyond Gerota’s fascia | |||
| Regional Lymph Nodes (N) | ||||
| N1 | Metastasis in 1 regional lymph node | |||
| N2 | Metastasis in > 1 regional lymph node | |||
| Distant Metastases (M) | ||||
| M1 | Distant metastasis present | |||
| Anatomic Stage | ||||
| Stage I | T1 | N0 | M0 | |
| Stage II | T2 | N0 | M0 | |
| Stage III | T1/T2 T3 |
N1 N0/N1 |
M0 M0 |
|
| Stage IV | T4 Any T |
Any N Any N |
M0 M1 |
|
| Reprinted with permission from Springer (American Joint Committee on Cancer. Kidney. In: Edge SB, Byrd DR, Compton CC, et al., eds. AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 7th ed. New York, NY: Springer; 2010479-89). | ||||
Advertisement
Prognostic Criteria
The Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center prognostic criteria are commonly used in patients with metastatic disease. These criteria correlate the following features with poor outcomes in patients treated with either cytokines or chemotherapy agents in various clinical trials before the era of targeted therapy:
- Poor performance status (Karnofsky performance status < 80%)
- Elevated LDH (> 1.5 × upper limit of normal)
- Elevated corrected calcium (> 10 mg/dL)
- Low hemoglobin (below lower limit of normal)
- Time from initial RCC diagnosis to the start of interferon-alpha therapy of < 1 year.
These risk factors categorize patients’ prognoses into favorable (0 risk factors), intermediate (1-2 risk factors), and poor (3-5 risk factors) risk groups, which were associated with a median survival of 30, 14, and 5 months, respectively.22
Cleveland Clinic has developed another prognostic model for patients with metastatic clear-cell RCC treated with vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-targeted therapy. This single-institution, retrospective study found the following to be predictors of poor outcome:
- An interval from diagnosis to treatment < 2 years
- Baseline corrected serum calcium < 8.5 mg/dL or > 10 mg/dL
- Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status > 0
- Neutrophil count > 4.5 × 109/LM
- Platelet count > 300 × 109/L
The median progression-free survival (PFS) in patients with 0 or 1 adverse prognostic factors was 20.1 months compared with 13 months in patients with 2 adverse prognostic factors and 3.9 months in those with 3 or more adverse prognostic factors.23
In another study, the outcomes data from the phase III trial in which sunitinib was compared with interferon-alpha were used to derive a prognostic model for those treated with sunitinib alone (n = 375). A prognostic nomogram was created by using 11 factors, including corrected serum calcium, number of metastatic sites, hemoglobin, prior nephrectomy, presence of lung metastases, presence of liver metastases, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status, thrombocytosis, time from diagnosis to treatment, alkaline phosphatase, and LDH.24
Although various prognostic models exist, robust clinical and biologic features predictive of outcome in patients with metastatic RCC are scarce. Until appropriate predictive patient variables are identified, available effective agents should be offered even to patients with poor prognoses. Targeted therapies against the VEGF pathway have significantly extended the lives of patients with advanced disease. The median overall survival (OS) duration now exceeds 2 years.1 Overall, the estimated average 5-year survival rates for patients with RCC are 96% for those presenting with stage I disease, 82% for those with stage II, 64% for stage III, and 23% for stage IV.
Patient Care
Treatment and Outcomes
Once a cardiac catheterization has been performed, the three most common therapeutic options are medical therapy, percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), and coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG).
Stage IA. For tumors ≤ 4 cm in diameter, surgical excision by partial nephrectomy (nephron-sparing surgery) (Figure 2) is recommended. The surgical approach can be either open or laparoscopic, depending on surgeon preference, and tumor size and location. The objective of surgery is to spare as many functioning nephrons as possible and to preserve renal function while excising the tumor. Radical nephrectomy is recommended only if the tumor is not amenable to partial nephrectomy.
In patients with decreased life expectancy (or those considered to be at high risk during surgery), options include active surveillance and thermal ablation (cryoablation or radiofrequency ablation). Although distant recurrence-free survival rates are comparable, thermal ablation has been associated with an increased risk of local recurrence compared with conventional surgery.25,26
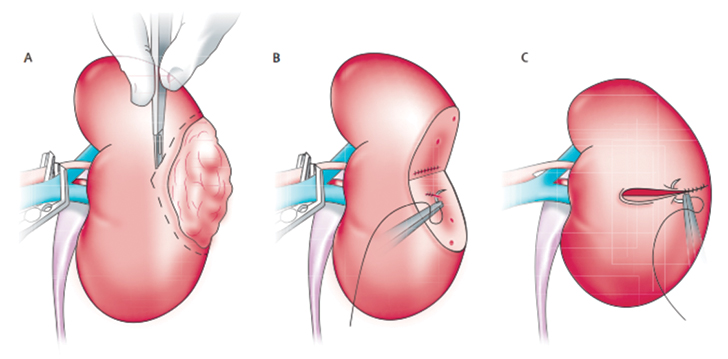
|
|
Figure 2. Partial Nephrectomy Surgical Technique in a Patient with Localized Kidney Cancer. Reprinted with permission from Elsevier (Rini BI, Campbell SC, Escudier B. Renal cell carcinoma. Lancet. 2009;373[9669]:1119-1132). Copyright © 2009 Elsevier. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/journal/01406736 |
Stage IB. For 4- to 7-cm tumors, partial nephrectomy, if feasible, or radical nephrectomy is the standard of care.
Stage II and III. Locally advanced tumors are managed with radical nephrectomy, which can require resection of adjacent organs, and with tumor thrombectomy from the renal vein and possibly the inferior vena cava.6 Between 40% and 60% of patients can be cured with such an aggressive surgical approach.27,28
After surgical excision, up to 30% of patients with localized tumors experience relapse. The lung is the most common site of distant recurrence, seen in 50% to 60% of patients. The median time to relapse after surgery is approximately 2 years, with most relapses occurring within 5 years. Interferon-alpha and high-dose interleukin-2 (IL-2) have been tested as adjuvant treatments following resection of stage I-II kidney cancer. However, no benefit has been seen in randomized trials.29,30 Observation remains standard care after nephrectomy, and eligible patients should be offered enrollment in randomized clinical trials.
The National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) Kidney Cancer Panel has recommended that patients be seen every 6 months for the first 2 years after surgery and annually thereafter. Each visit should include a history, physical examination, and comprehensive metabolic panel (eg, blood urea nitrogen, serum creatinine, calcium levels, LDH, and liver function tests). Abdominal and chest imaging studies should be done approximately 2 to 6 months after surgery and as clinically indicated thereafter.31
Stage IV. Cytoreductive nephrectomy before systemic therapy is recommended in patients with a surgically resectable primary tumor.32 Metastasectomy should be considered in patients with favorable features such as a solitary metastasis or a long interval between initial diagnosis and the development of metastatic disease. In these patients, the 5-year disease-free survival rate can be as high as 30%.
Systemic therapy is recommended for patients with residual metastatic disease, though patients with low-volume indolent metastases may initially undergo a period of observation. Several systemic agents exist today that are non-curative and therefore require long-term sequential therapy with multiple agents and management of toxicity.
Immunotherapy
- IL-2. In selected patients with relapsed or medically unresectable stage IV clear-cell RCC, high-dose IL-2 can be considered as a first-line treatment option. Although no demonstrable OS or PFS benefit has been seen, durable complete remissions occur in 7% to 8% of patients. Thus, despite the associated toxicity of capillary leak syndrome, IL-2 remains a viable treatment option reserved for patients with good performance status and acceptable comorbid disorders.6 Unfortunately, there are no predictive biomarkers upon which to base the selection of patients for treatment with high-dose IL-2.
- Bevacizumab plus interferon-alpha. This combination has been associated with a 31% objective response rate with a median PFS of 10.2 months. The regimen is listed as a first-line treatment option for patients with clear-cell RCC with a category 1 designation.
Targeted therapy
Targeted therapy with tyrosine kinase inhibitors has been used widely in first- and second-line treatments. To date, 7 such agents have been approved by the FDA for the treatment of advanced RCC: sunitinib, sorafenib, pazopanib, axitinib, temsirolimus, everolimus, and bevacizumab in combination with interferon.
- VEGF pathway inhibitors: sunitinib, pazopanib, and bevacizumab plus interferon-alpha are listed as first-line treatment options with a category 1 designation. Sorafenib and axitinib are approved as second-line options.
- Sunitinib. This multi-kinase inhibitor of VEGF and related receptors has been linked to an advantage in independently assessed objective response rate (39% vs 8%; P < 0.001), median PFS (11 months vs 5 months, P < 0.001), and median OS (26.4 months vs 21.8 months, P = 0.051) vs interferon-alpha in a phase III trial.1 The trial included untreated patients with metastatic RCC (n = 750) who were given either sunitinib or interferon-alpha. Common toxicities were fatigue, mucositis, hand-foot syndrome, diarrhea, hypertension, and hypothyroidism.
- Pazopanib. An oral angiogenesis inhibitor targeting VEGFR-1, -2 and -3, PDGFR-alpha and -beta, and c-KIT, pazopanib has shown promise in a phase III trial. Patients with advanced clear-cell RCC (n = 475) with no prior treatment or one prior cytokine-based treatment were randomly assigned 2:1 to receive either pazopanib or placebo. Progression-free survival averaged 9.2 months in the pazopanib group vs 4.2 months in the placebo group.33 The objective response rate was 30% with pazopanib and 3% with placebo (all results were statistically significant). Common adverse reactions included diarrhea, hypertension, hair-color changes, nausea, anorexia, vomiting, fatigue, abdominal pain, and headache. Hepatotoxicity was notable as a grade 3 toxicity, therefore it is critical to monitor liver function before and during treatment. Pazopanib also has been associated with a prolonged QTc interval.
- Bevacizumab. A monoclonal antibody that binds to and neutralizes circulating VEGF protein,34 bevacizumab plus interferon-alpha has been associated with a 31% objective response rate with a median PFS of 10.2 vs 5.4 months (hazard ratio, 0.63; 95% CI, 0.52-0.75; P = 0.0001) vs interferon-alpha alone. This benefit was observed irrespective of risk group or whether reduced-dose interferon-alpha was given. In the US, a similar trial performed by the Cancer and Leukemia Group B, also demonstrated a PFS advantage in patients receiving bevacizumab. There was significantly more grade 3 to 4 hypertension, anorexia, fatigue, and proteinuria in patients receiving bevacizumab plus interferon-alpha. Patients who developed hypertension on bevacizumab plus interferon-alpha had significantly improved PFS and OS vs patients without hypertension.35
- Sorafenib. A small molecule inhibitor of VEGF and related receptors, sorafenib has been linked to extended PFS in patients with RCC. In a phase III trial, 905 patients with treatment-refractory metastatic RCC were randomly assigned to receive either oral sorafenib 400 mg twice a day or placebo. Patients in the sorafenib group had 5.5 months of PFS vs 2.8 months for those in the placebo group (P < 0.0001).36
- Axitinib. A selective, second-generation inhibitor of VEGFR-1, -2, and -3, axitinib is a category 1 recommendation by the NCCN Kidney Cancer Panel in patients in whom 1 prior systemic therapy has failed. The approval was based on a multicenter, randomized phase III study comparing patients treated with axitinib vs sorafenib following first-line therapy with sunitinib, bevacizumab plus interferon-alpha, temsirolimus, or cytokines. The median PFS was 6.7 months for patients who received axitinib compared with 4.7 months in those who received sorafenib (hazard ratio, 0.665; 95% CI, 0.544-0.812; one-sided P < 0.0001). Treatment was discontinued because of toxic effects in 14 (4%) of 359 patients treated with axitinib and 29 (8%) of 355 patients treated with sorafenib. The most common adverse events were diarrhea, hypertension, and fatigue in the axitinib arm, and diarrhea, palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia, and alopecia in the sorafenib arm.37
- mTOR inhibitors
- Temsirolimus. An inhibitor of mTOR, a molecule implicated in several tumor-promoting intracellular signaling pathways, temsirolimus has been included by the NCCN Kidney Cancer Panel as a category 1 recommendation for first-line treatment of patients with poor prognosis and relapsed or medically unresectable, predominantly clear-cell stage IV RCC.31 Patients (n = 626) were randomly assigned to temsirolimus 25 mg per week IV vs interferon alone vs temsirolimus 15 mg per week IV plus interferon. Patients treated with temsirolimus had a longer overall survival than those who received interferon monotherapy (10.9 months vs 7.3 months, P = 0.003).38 Adverse events include rash, stomatitis, pain, infection, peripheral edema, thrombocytopenia and neutropenia, hyperlipidemia, hypercholesterolemia, and hyperglycemia.
- Everolimus. An orally administered inhibitor of mTOR, everolimus is approved as a second-line therapy after treatment with sorafenib or sunitinib has failed.31 In the RECORD 1 trial, an international, multicenter, double blind, randomized phase III trial, everolimus was compared with placebo for the treatment of metastatic RCC in patients whose disease had progressed during treatment with sunitinib or sorafenib. Patients (n = 410) were randomly assigned 2:1 to receive either everolimus or placebo. The primary end point was PFS. According to the updated results of this trial, median PFS determined by independent central review was 4.9 months for everolimus vs 1.9 months (95% CI, 1.8-1.9) for placebo.39 Common adverse events include stomatitis, rash, and fatigue. Pneumonitis is an uncommon but serious side effect presenting as dyspnea.
Summary
- Renal cell carcinoma consists of a heterogeneous group of tumors with distinct genetic and metabolic defects, and histopathologic and clinical features.
- In localized disease, partial nephrectomy for small tumors and radical nephrectomy for large tumors continue to be the gold-standard treatments.
- Cytoreductive nephrectomy is often indicated before the start of systemic treatment in appropriately selected patients with metastatic disease.
- Immunotherapy (high-dose IL-2) is mainly reserved for patients with a good prognosis and is administered on the basis of a durable complete response rate.
- Targeted drugs, including inhibitors of VEGF and mTOR, offer new effective therapeutic options for patients with metastatic disease.
References & Suggested Readings
References
- Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Tomczak P, et al. Overall survival and updated results for sunitinib compared with interferon alfa in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27(22):3584-3590.
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2012;62(1):10-29.
- Nguyen MM, Gill IS, Ellison LM. The evolving presentation of renal carcinoma in the United States: trends from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results program. J Urol. 2006;176(6 Pt 1):2397-2400.
- Stafford HS, Saltzstein SL, Shimasaki S, Sanders C, Downs TM, Sadler GR. Racial/ethnic and gender disparities in renal cell carcinoma incidence and survival. J Urol. 2008;179(5):1704-1708.
- Chow WH, Devesa SS, Warren JL, Fraumeni JF Jr. Rising incidence of renal cell cancer in the United States. JAMA. 1999;281(17):1628-1631.
- Rini BI, Campbell SC, Escudier B. Renal cell carcinoma. Lancet. 2009;373(9669):1119-1132.
- Hollingsworth JM, Miller DC, Daignault S, Hollenbeck BK. Rising incidence of small renal masses: a need to reassess treatment effect. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2006;98(18):1331-1334.
- Chow WH, Dong LM, Devesa SS. Epidemiology and risk factors for kidney cancer. Nat Rev Urol. 2010;7(5):245-257.
- Siegel R, Ward E, Brawley O, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2011: the impact of eliminating socioeconomic and racial disparities on premature cancer deaths. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61(4):212-236.
- Hunt JD, van der Hel OL, McMillan GP, Boffetta P, Brennan P. Renal cell carcinoma in relation to cigarette smoking: meta-analysis of 24 studies. Int J Cancer. 2005;114(1):101-108.
- Chow WH, Gridley G, Fraumeni JF Jr, Järvholm B. Obesity, hypertension, and the risk of kidney cancer in men. N Engl J Med. 2000;343(18):1305-1311.
- Benichou J, Chow WH, McLaughlin JK, Mandel JS, Fraumeni JF Jr. Population attributable risk of renal cell cancer in Minnesota. Am J Epidemiol. 1998;148(5):424-430.
- Gordon SC, Moonka D, Brown KA, Rogers C, Huang MA, Bhatt N, Lamerato L. Risk for renal cell carcinoma in chronic hepatitis C infection. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2010;19(4):1066-1073.
- Ishikawa I, Saito Y, Asaka M, et al. Twenty-year follow-up of acquired renal cystic disease. Clin Nephrol. 2003;59(3):153-159.
- Rakowski SK, Winterkorn EB, Paul E, Steele DJ, Halpern EF, Thiele EA. Renal manifestations of tuberous sclerosis complex: Incidence, prognosis, and predictive factors. Kidney Int. 2006;70(10):1777-1782.
- Clague J, Lin J, Cassidy A, Matin S, Tannir NM, Tamboli P, et al. Family history and risk of renal cell carcinoma: results from a case-control study and systematic meta-analysis. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2009;18(3):801-807.
- Linehan WM, Srinivasan R, Schmidt LS. The genetic basis of kidney cancer: a metabolic disease. Nat Rev Urol. 2010;7(5):277-285.
- Janus CL, Mendelson DS. Comparison of MRI and CT for study of renal and perirenal masses. Crit Rev Diagn Imaging. 1991;32(2):69-118.
- Hricak H, Demas BE, Williams RD, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis and staging of renal and perirenal neoplasms. Radiology. 1985;154(3):709-715.
- Park JW, Jo MK, Lee HM. Significance of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron-emission tomography/computed tomography for the postoperative surveillance of advanced renal cell carcinoma. BJU Int. 2009;103(5):615-619.
- Shannon BA, Cohen RJ, de Bruto H, Davies RJ. The value of preoperative needle core biopsy for diagnosing benign lesions among small, incidentally detected renal masses. J Urol. 2008;180(4):1257-1261.
- Motzer RJ, Bacik J, Murphy BA, Russo P, Mazumdar M. Interferon-alfa as a comparative treatment for clinical trials of new therapies against advanced renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20(1):289-296.
- Choueiri TK, Garcia JA, Elson P, et al. Clinical factors associated with outcome in patients with metastatic clear-cell renal cell carcinoma treated with vascular endothelial growth factor-targeted therapy. Cancer. 2007;110(3):543-550.
- Motzer RJ, Bukowski RM, Figlin RA, et al. Prognostic nomogram for sunitinib in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Cancer. 2008;113(7):1552-1558.
- Campbell SC, Novick AC, Belldegrun A, et al, and the Practice Guidelines Committee of the American Urological Association. Guideline for management of the clinical T1 renal mass. J Urol. 2009;182(4):1271-1279.
- Kunkle DA, Uzzo RG. Cryoablation or radiofrequency ablation of the small renal mass: a meta-analysis. Cancer. 2008;113(10):2671-2680.
- Blute ML, Leibovich BC, Lohse CM, Cheville JC, Zincke H. The Mayo Clinic experience with surgical management, complications, and outcome for patients with renal cell carcinoma and venous tumour thrombus. BJU Int. 2004;94(1):33-41.
- Margulis V, Sánchez-Ortiz RF, Tamboli P, Cohen DD, Swanson DA, Wood CG. Renal cell carcinoma clinically involving adjacent organs: experience with aggressive surgical management. Cancer. 2007;109(10):2025-2030.
- Clark JI, Atkins MB, Urba WJ, et al. Adjuvant high-dose bolus interleukin-2 for patients with high-risk renal cell carcinoma: a cytokine working group randomized trial. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21(16):3133-3140.
- Messing EM, Manola J, Wilding G, et al, and the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group/Intergroup trial: Phase III study of interferon alfa-NL as adjuvant treatment for resectable renal cell carcinoma: an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group/Intergroup trial. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21(7):1214-1222.
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Kidney Cancer Guidelines Version 2.2012. 2012. Available at: http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/kidney.pdf. Accessed July 31, 2012.
- Flanigan RC, Mickisch G, Sylvester R, Tangen C, Van Poppel H, Crawford ED. Cytoreductive nephrectomy in patients with metastatic renal cancer: a combined analysis. J Urol. 2004;171(3):1071-1076.
- Sternberg CN, Davis ID, Mardiak J, et al. Pazopanib in locally advanced or metastatic renal cell carcinoma: results of a randomized phase III trial. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(6):1061-1068.
- Presta LG, Chen H, O’Connor SJ, et al. Humanization of an anti-vascular endothelial growth factor monoclonal antibody for the therapy of solid tumors and other disorders. Cancer Res. 1997;57(20):4593-4599.
- Rini BI, Halabi S, Rosenberg JE, et al. Bevacizumab plus interferon alfa compared with interferon alfa monotherapy in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: CALGB 90206. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(33):5422-5428.
- Escudier B, Eisen T, Stadler WM, et al, and the TARGET Study Group. Sorafenib in advanced clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2007;356(2):125-134.
- Rini BI, Escudier B, Tomczak P, et al. Comparative effectiveness of axitinib vs sorafenib in advanced renal cell carcinoma (AXIS): a randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2011;378(9807):1931-1939.
- Hudes G, Carducci M, Tomczak P, et al, for the Global ARCC Trial. Temsirolimus, interferon alfa, or both for advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2007;356(22):2271-2281.
- Motzer RJ, Escudier B, Oudard S, et al, for the RECORD-1 Study Group. Phase III trial of everolimus for metastatic renal cell carcinoma: final results and analysis of prognostic factors. Cancer. 2010;116(18):4256-4265.
- DeVita VT Jr, Lawrence TS, Rosenberg SA, eds. Cancer: Principles & Practice of Oncology: Primer of the Molecular Biology of Cancer. Philadelphia, PA. Lippincott, Williams, and Wilkins, 2011.
Suggested Readings
- DeVita VT, Hellman S, Rosenberg SA. Cancer, Principles & Practice of Oncology. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2005.
- Abraham J, Gulley JL, Allegra CJ. Bethesda Handbook of Clinical Oncology. 3rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2010.
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Kidney Cancer Guidelines Version 2.2012. 2012. Available at: http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/kidney.pdf. Accessed July 31, 2012.
